Dental Bridges In Palm Beach Gardens
Dental Bridges In Palm Beach Gardens
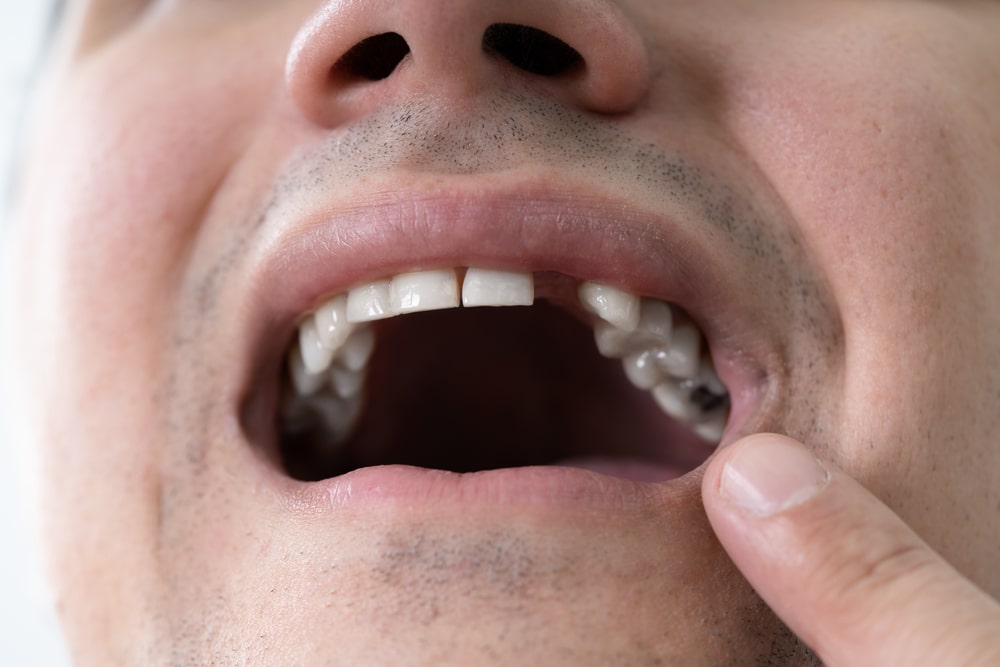
Tooth loss can take a toll on more than your appearance, affecting how you chew, speak, and even the way your face is shaped over time.
At Lerner & Lemongello in Palm Beach Gardens, FL, we offer custom dental bridges as a reliable, long-term solution for restoring both function and appearance. Dr. Gerard J. Lemongello brings over 35 years of experience in cosmetic and restorative dentistry and is an accredited American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry member. As a senior clinical instructor at NYU’s Rosenthal Institute, Dr. Lemongello combines advanced training with artistic precision to deliver results that look and feel natural.
What Are Dental Bridges?
A dental bridge is a form of dental restoration designed to literally “bridge the gap” left by one or more missing teeth. Unlike removable partial dentures, dental bridges are fixed in place and offer long-term stability and function.
Each bridge is made up of two main parts: the abutments and the pontics. Abutments are crowns fitted onto the natural teeth or implants that sit on either side of the gap. Positioned on either side of the missing tooth, the abutments are crowns placed on existing teeth or dental implants. Dental bridges are a time-tested method many patients prefer for their durability, aesthetic appeal, and how they seamlessly integrate with the rest of the teeth.
The Advantages of Dental Bridges
Patients in Palm Beach Gardens who choose dental bridges often do so for their wide range of benefits:
- They restore your smile by closing the gaps created by missing teeth.
- They improve your ability to chew and speak clearly.
- They help maintain the natural shape of your face by preventing muscle tone loss.
- They evenly distribute the force of your bite, reducing strain on other teeth.
- They prevent remaining teeth from shifting out of alignment, which can lead to bite issues and further tooth loss.
Choosing a dental bridge not only improves your smile but also supports long-term oral health.
Patient Testimonial
“My experience regarding the entire procedure was fantastic. I allowed Drs. Lerner and Lemongello to utilize me as a patient to teach other dentists from around the world their expertise while being treated. I never realized the extraordinary skill they possess and would truly recommend them to anyone considering a new smile. They are truly the world’s best.” -M.F.
Types of Dental Bridges We Offer
We offer several types of bridges to match each patient’s specific needs:
- Traditional Dental Bridges: These are the most common type and consist of dental crowns on either side of the missing tooth, with a pontic in between.
- Cantilever Bridges: Ideal when there are healthy teeth on only one side of the gap, these bridges are supported by a single abutment.
- Maryland Bonded Bridges: These use a metal or porcelain framework with “wings” bonded to the back of adjacent natural teeth. They’re often used for front teeth due to their conservative design.
Every dental bridge is carefully designed to match the shape, size, and color of your natural teeth for a flawless, natural look.
What to Expect During the Dental Bridge Process
Getting a dental bridge at Lerner & Lemongello is a two-visit process. At your initial visit, the abutment teeth will be carefully reshaped to support the bridge, followed by precise impressions sent to a dental lab for fabrication. In the meantime, you’ll receive a temporary bridge to protect your teeth and maintain function.
At your second visit, we remove the temporary bridge and carefully fit the permanent one. Once we confirm the fit, bite alignment, and aesthetics, your new dental bridge will be securely cemented in place.
How Long Do Dental Bridges Last?
When cared for properly, dental bridges are a long-lasting solution—often remaining in place for a decade or more. Keeping up with brushing, flossing, and check-ups is essential to their longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I Eat Normally With a Dental Bridge?
Once your bridge is securely in place, you’ll be able to eat most of your favorite foods again. It’s best to avoid very sticky or hard foods, especially during the adjustment period.
How Do I Care for a Dental Bridge?
Maintaining a dental bridge involves brushing and flossing daily, just like your natural teeth. To keep the area under your bridge clean, your dentist may provide specific tools like floss threaders or interdental brushes.
Will a Dental Bridge Affect the Way I Speak?
Some patients notice slight speech differences initially, but this typically resolves within a few days. Your tongue quickly adapts to the presence of the bridge.
How Much Do Dental Bridges Cost?
The cost of dental bridges can vary depending on the type of bridge, the materials used, and the complexity of your case. For a detailed estimate and to explore your options, we encourage you to visit our financing page to learn more about flexible payment solutions.
Why Choose Dr. Gerard J. Lemongello for Dental Bridges?
Dr. Gerard J. Lemongello brings over 35 years of hands-on experience in cosmetic and restorative dentistry, making him a trusted expert in designing and placing dental bridges.
A graduate of the University of Florida College of Dentistry and an accredited member of the American Academy of Cosmetic Dentistry, Dr. Lemongello has dedicated his career to mastering advanced techniques that deliver natural-looking, long-lasting results. His role as a senior clinical instructor at NYU’s Rosenthal Institute and ongoing education at top institutes nationwide ensure he remains at the forefront of restorative care.
Patients in Palm Beach Gardens choose Dr. Lemongello for his ability to blend function with artistry—creating custom dental bridges that restore missing teeth, enhance appearance, and support long-term oral health with precision and care.
Expert Dental Restoration Services in Palm Beach Gardens, FL
If you’re missing teeth and exploring dental restoration options, now is the perfect time to take the next step. At Lerner & Lemongello, we’re here to help you regain a healthy, confident smile with expert, personalized care.
Contact our Palm Beach Gardens office at 561-627-9000 to schedule your consultation with Dr. Lemongello, or fill out our convenient online contact form, and we’ll be in touch soon.